The birthplace of watermelon is the semi-desert of hot South Africa. However, today this plant of the pumpkin family with bright and juicy, sweet fruits is grown everywhere. The northern border of the spread of this culture, through the efforts of breeders, has shifted significantly to the northern latitudes. The territory of Belarus was no exception. With an abundance of varieties and hybrids that have passed the test of the climate of the East European Middle Band, even the inexperienced melon grower can treat himself and those close to him with a sweet and healthy watermelon from his garden.
Varieties optimal for cultivation in Belarus
Not every kind of culture so atypical for Belarus as a watermelon will delight a gardener. Watermelon is still a southern plant, light and thermophilic, in need of sun and moderate moisture. Watermelon will not be able to grow and develop normally at temperatures below +15aboutC. Therefore, in conditions when such a decrease in temperature is not uncommon in the warm summer months, it is appropriate to opt for early and mid-early varieties. Specify how many days the plant will need from the onset of fruit ovaries to the ripening of the fruit. This period should not exceed 70-80 days. Based on this, the following varieties and hybrids are recommended to Belarusian gardeners.
Table: varieties and hybrids of watermelon for open ground
| Title | Period vegetation (days) | Short description |
| Madison | 65-85 | The weight of the fetus is up to 3-6 kg. Fruits are elongated, light green, with dark narrow stripes, thin-skinned. The core is bright red, sugar, juicy. Drought tolerant. Resistant to Fusarium. |
| Stetson F1 | 65-75 | The weight of the fetus is 3-5 kg. Spherical berries. Powerful, branched lashes. The peel is of medium thickness. The core is sweet, without fibers. High yielding. Does not suffer from temperature changes. |
| Top Gun F1 | 55-75 | The weight of the fetus is 4-6 kg. The berries are elliptical, glossy. The peel is thin. The core is raspberry, sweet. The seeds are small. |
| Crimson Ruby | 65-70 | Fruits weighing 3-5 kg, elongated. The peel is of medium thickness, light green with dark spots and stripes. The core is bright, juicy, sugar. Veins and fibers are absent. Resistant to Fusarium. Not afraid of sunburn. |
| Charleston Gray | 75-90 | There are few ovaries, but the berries are large, weighing 3-8 kg, of an original torpedo shape. The peel is thick, hard, monotonous, salad shade. The core is bright pink, juicy, sweet. The plant is resistant to anthracnose and fusarium. |
| Romanza F1 | 70-85 | Fruits are spherical, weighing 3-8 kg. Raspberry core, tender, juicy, sweet. The plant forms powerful whips. The variety is resistant to temperature drops, not susceptible to Fusarium. |
Table: varieties and hybrids of watermelon for greenhouse cultivation
Due to limited space, varieties that do not form powerful, long lashes are selected for growing watermelons in a greenhouse. The fruits of such plants are small, within 2-6 kg. The compactness of the plant also facilitates the task of artificial pollination of flowers.
| Title | Period vegetation (days) | Short description |
| Katherine | 70-75 | The weight of the fruit is 2-4 kg. Watermelons are elliptical, barrel-shaped. The rind is yellowish, with fuzzy dark green stripes. The core is dense, dark red, sugar. The plant is resistant to fusarium. |
| Early Kuban | 75-85 | The weight of watermelons is 1.5-3 kg. Fruits with a segmented surface. The peel is thin. The core is grainy, sweet. The plant does not form powerful lashes. High resistance to bacteriosis, anthracnose and fusariosis. |
| Libya | 75-85 | Berries weighing up to 3-6 kg, widely elliptic. The peel is thin, light green with dark wide stripes. The core is red, moderately sweet. The plant is resistant to sunburn and temperature changes. |
| Twinkle | 75-85 | The weight of the fruit is 1.5-2.5 kg. Shoots with copious ovaries. The peel of the berry is thin, the core is juicy, sugar. Less susceptible to Fusarium. |
| Gift the sun | 65-75 | The fruits are round, weighing 1.5-3 kg. The peel is fragile, thin, yellow with dark yellow stripes. The pulp is scarlet, granular, tender, sugar. The seeds are small. Drought tolerant. |
Growing conditions
Watermelon is a southern culture, thermophilic. This plant will not be able to grow with a lack of heat, light and moisture.
Soils for watermelon beds are preferably sandy loam or loamy, light, rich in humus. Heavy, waterlogged soils are unacceptable. The optimum pH value is in the range of 6 - 6.5. Watermelon grows well in areas where legumes and grains, carrots and cabbage were previously grown, but after pumpkins, cucumbers or zucchini, watermelons should not be planted. For a watermelon, crop rotation is important, as is the prevention of bacteriosis, a disease transmitted by soil bacteria.
Watermelon is demanding for proper watering. Overmoistening will lead to the development of such fungal diseases as gray rot, anthracnose, fusarium. The pulp of a ripe fruit will be loose, with low palatability. Do not over-moisten the plants in cool, damp, rainy weather. During fruit ripening, watering is stopped completely. Watermelon is a drought-tolerant plant, however, a lack of moisture can also cause the lash to dry out, and reduce yield and fruit mass.
The plant has a powerful core root system, therefore, does not tolerate stagnation of water. The area where the watermelons grow should be well-drained. In places where groundwater lies close to the surface, it is better to refuse to grow watermelons.
Watermelon is photophilous. Plants should be planted, adhering to the planting scheme for open ground or greenhouses, at the recommended distance between them. No more than one plant is planted in one hole: no more than three watermelons should grow per square meter. It is useful to limit fruiting depending on insolation conditions and humidity. Thickening of landings must not be allowed.
Growing watermelon seedlings
In the Belarusian climate, the most reliable way to grow watermelon is seedlings.
When to plant seeds for seedlings
Begin preparing seedlings in the middle or near the end of April. To do this, the seeds are soaked for 10-15 minutes in warm water, and then spread in a previously prepared container with a flat bottom (tray, plate, tray). It is convenient to use disposable plastic utensils. At the bottom, place a thin layer of cotton wool - it will protect the seeds from drying out. Gauze with seeds is placed on top of the cotton wool until they germinate. From time to time, the container is wetted with either water or a biostimulant solution (for example, Zircon).

Germinated seeds
Seedling Care
Hatching seeds are transplanted into peat or pots or plastic cups filled with universal soil. You can prepare the mixture yourself. To do this, you need a garden turf, humus and sand in a ratio of 5: 3: 2. 1 liter of sifted ash or crushed chalk is added per liter of such a mixture. Before planting seeds in a tank, the soil is moistened.
The seeds are deepened by 5 cm, one in each pot, once again moderately watered, covered with a film or glass on top. The containers are exposed in a dark place with room temperature. To prevent rot and mold, from time to time the film or glass is removed, ventilating the seedlings.

Watermelon seedlings in plastic cups
Shoots appear in 10-14 days. From this moment, the seedlings are kept in a bright and warm place, providing additional illumination if necessary. To harden seedlings for 10 days, the temperature in the room is reduced to 16 - 18aboutC, and then again increased to 20 - 22aboutFROM.
Watered infrequently, but plentifully. After the formation of the first two true leaves, the seedlings are fed with a complex fertilizer for seedlings (Rostock, Kemira-lux).
Transplanting seedlings into the ground
Ready for transplantation, watermelon seedlings should reach a height of 12-14 cm and have 4-6 true leaves. 8-10 days before transplanting to a permanent place, seedlings are taken out for acclimatization in a greenhouse (or outside), gradually increasing the time to 6 hours.

Hardening watermelon seedlings outdoors
For planting plants in the ground choose a warm, but not sunny day. Each plant is planted in a hole with a diameter of 25-30 cm and a depth in size of the tank with seedlings. At the bottom of each hole put a tablespoon of ash and a handful of compost, pour plenty of warm water. Seedlings grown in peat pots are lowered into the hole with them. From plastic cups, seedlings are carefully removed with the soil. The plant is deepened to cotyledon leaves.

A plant that has formed 4-6 true leaves can be transplanted into the ground.
Growing watermelon seeds
The site for the watermelon plantation should be protected from the north and north-east winds, warmed up by the sun and not suffer from stagnation of moisture after rains. Having picked up a site suitable for plants, in the fall they prepare it for planting. First, peeling (loosening of the topsoil) to a depth of 12 cm is carried out. The purpose of the peeling is to destroy weed residues and to turn weed seeds to the surface in order to provoke their germination. Peeling will save the site from soil insect pests. On large areas, peeling is carried out mechanically, in the garden beds you can get by with a hoe or garden pitchfork. 12-14 days after peeling, they begin to plow the site. During this period, potash, magnesium and phosphorus fertilizers are applied per 1 sq.m - 40 g of superphosphate, 30 g of ammonium sulfate and 20 g of potash fertilizers. The next year, the soil is loosened twice - in early spring and immediately before planting seeds.
Planting watermelon seeds in open ground
Seeds are kept in warm water until they swell. Landing is carried out at a temperature not lower than 14aboutFROM. Wells are arranged according to a 140x60 cm pattern. Seats are fertilized at the rate of 1 tablespoon of ash and 1 teaspoon of nitroammophosphate per well. Seeds close up to a depth of 7-8 cm. Sprouts appear after 8-10 days.
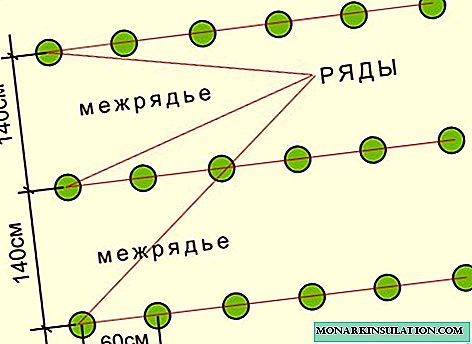
1111122
After planting the seeds, the wells are mulched - sprinkled with soil, or lay a plastic film with holes on top of the beds.

Outdoor watermelon shoots
Mulching with a film will require additional costs and labor, but it will protect plantings from pests and weeds, ensure uniform heating of the soil and the preservation of heat and moisture, which will increase the yield of watermelons.

Watermelon bed mulched with a film cloth
Planting watermelon seeds in a greenhouse
The place for the watermelon greenhouse is chosen sunny, the greenhouse should not be located in the shade of trees or buildings. You can not put a greenhouse on the northern slope of the site or in the lowland. The place for the greenhouse should be dry, well-drained.
Prepare a greenhouse in the fall. The soil for planting is fed with rotted manure and mowed grass, dug up and left until spring. By the time the seeds are planted, the greenhouse substrate will be ready. Wells for seeds are placed on the meter-wide beds according to the scheme 100x50 cm, either in one row or in a checkerboard pattern. Fertilizers are added to each well, as for growing in open ground.

Planting watermelons staggered
As the lashes of plants grow, they are tied to twine stretched along the greenhouse.

Watermelon plants planted in a row
Plant care
Watermelons planted in open ground and in a greenhouse will have to grow under different conditions of temperature, humidity and protection from atmospheric phenomena.
In the open ground
In order not to expose plants grown in the open ground to possible temperature changes in the spring, group or individual shelters from film or non-woven material are arranged. Such shelters also contribute to seed germination and protect plants from pests. Film shelters accelerate crop ripening.

Wire arches, twine and film - the simplest shelter from improvised means
The first watering is carried out when 5-6 leaves appear in plants. The second watering is during the flowering period. Then watermelons are watered as needed. Stop watering only before harvesting the fruit.
Care for watermelons in the open ground consists in weeding, top dressing, cultivation. To form additional roots, the whips are pinned to the ground and sprinkled with moist soil. Fruiting restriction is carried out, leaving 3-4 ovaries on each lash. This is useful for saving energy by the plant during fruit formation. In the hot summer, the watermelon does not need to be pinched - the more the green mass of the plant, the more sugar the fruit will gain.
In the greenhouse
During the growing season in a watermelon greenhouse spend 2-3 loosening. Watering is carried out similarly to planting in open ground, warm water, under the root of the plant. In hot weather, the greenhouse is aired daily. For pollination by insects during flowering, the greenhouse is left open during the day. Manually pollinate the plants in the morning.
On each watermelon lash, 2-4 ovaries are left. Weight-gaining fruits are placed in durable nets tied to the beams of the greenhouse.

Fruits gain weight
Watermelon dressing
The climatic conditions of Belarus require mandatory feeding of watermelons growing both in open ground and in the greenhouse. With the correct pre-planting preparation of the soil for watermelon beds - the introduction of the green mass of herbaceous plants - watermelons will not need to be fed. It is enough to treat the soil with Phytosporin to eliminate pathogens. The bulk of the fertilizer is applied during the flowering, setting and fruit development.
Table: preparations and terms of their introduction
| A drug | Application Time | number |
| Nutrivant Plus | Beginning of flowering | 2 kg per 200 liters of water |
| Calcite | Bloom | 800 gr per 100 l of water |
| Speedfall Amino Bloom | Bloom | 200 ml for 200 l of water |
| Boroplus | Beginning of fruiting | according to instructions |
| Megafol | Beginning of fruiting | 1 liter for 150 l of water |
| Uniflor micro | Active fruiting | 2 teaspoons on 10 l of water |
| Terraflex Station wagon | Active fruiting | 70 gr per 100 l of water |
| Nitrate calcium | Active fruiting | 80 gr per 100 l of water |
| Lignohumate potassium | Active fruiting | 100 gr for 300 l of water |
Before feeding plants, it is recommended to spill them with warm water. Fertilizing fertilizers for feeding with cold water should also not be. Loosening the soil is also a type of top dressing - due to loosening, the substances useful to the plant are more evenly distributed in the soil. Feeding watermelons is stopped when the fruits reach ripeness.
Diseases and pests of watermelon melon
- Anthracnose. Fungal disease. Symptoms: yellow-brown spots on the leaves, black and brown ulcers with a pinkish coating. General rotting and drying of the plant. Methods of control: treatment with Bordeaux liquid, benlat and cuprosan according to the instructions. Affected leaves and stems are removed.

Leaf of anthracnose infected plant
- Fusarium Fungal disease. Symptoms: wilting, decay of the basal part, lower parts of the lashes. Methods of control: destruction of diseased plants, soil disinfection.

Fusarium wilt
- White rot. Fungal disease. Symptoms: focal decay of plant areas, lashes, flowers and fruits. Ways of struggle: removal and destruction of rotten parts of a plant, treatment of lesions with a paste of potassium permanganate and chalk, treatment with powdered coal or lime. Spraying with a solution of copper sulfate.

White rot on the basal part of the stem
- Olive spotting. Fungal disease. Symptoms: olive ulcers on the lashes, spotting and deformation of the leaves, drying of the ovaries. Ways of struggle: treatment with Bordeaux liquid, cuprosan. Affected parts of the plant are removed and destroyed.
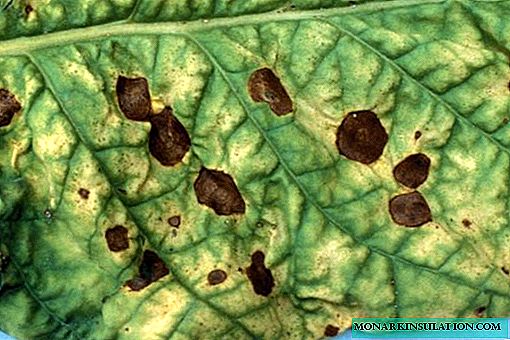
Ulcers and deformation on the leaf of a plant with olive spotting
- Bacteriosis. Bacterial pathogens. Symptoms: rot, ulcers, mucus-filled cracks in the fruits of the plant.Methods of control: preparations containing copper (use strictly according to the instructions).

Decay of the fetus caused by bacteriosis
- Wireworm. Signs: during ripening, through holes appear in them, the fruits rot. Control measures: traps with a bait from vegetables, planting in the aisles of mustard, legumes. If the pest is very common, plants are treated with preparations of Thunder-2, Zemlin, Provotox.

The wireworm and its larvae
- Gourd aphids. Signs: on the lower parts of the plant, especially on the leaves, clusters of small, 1-2 mm, black aphids are visible. Flowers and leaves wither, twist and fall. The general appearance of the plant is weakened, depressed. Control measures: sprinkling the plant with a mixture of tobacco dust and ash, spraying with infusion of fermented grass, soap solution.

Clump of gourds
- Mosaic. Viral disease. Symptoms: dark and light mosaic spots on the leaves, their deformation, tubercles and swelling on the fruits. Methods of control: destruction of diseased plants, soil disinfection.

Characteristic spots of watermelon mosaic
- Spider mite. Signs: the leaves are covered with brown dots, the tops of the shoots and flowers are tightened with thin threads, the affected parts turn yellow and dry. The pests themselves are subtle. Control measures: drugs Actofit, Neoron, Agravertin, Apollo. To get rid of the tick, you will need a course of 3-5 procedures.

Spider mite plant
- Thrips. Symptoms: small black-brown strokes on the leaves. In these places, the tissues acquire a silver-gray color and die. The flowers are falling. Control measures: glue traps, infusion of chamomile, tomato tops, celandine. In advanced cases, Verimek, Karate, Fitoverm drugs are used. To destroy the pest, you will need a course of 3-4 treatments.

Thrips infection on a plant leaf
Harvesting and storage
In hot summer, the time for ripening watermelons comes earlier, cool - later. A reliable indicator of berry ripeness - the seeds acquire hardness and the color characteristic of this watermelon variety. External indicators of the watermelon's readiness for harvesting are a dried stalk, a yellow spot on the side of the fruit. The peel becomes glossy, resilient, with a clear contrasting pattern. When you click on the peel of a watermelon, a characteristic dull sound is heard - the fruit has become juicy. When pressed, the watermelon crackles slightly.

Watermelons with characteristic ripeness
It is important not to miss the moment of ripening - overripe watermelons quickly rot. Ripe berries are cut from the stems with a sharp knife, leaving 5 cm of the stalk. Hands should not be plucked - the place of plucking can rot. The harvesting of watermelons, as a rule, begins in the second or third decade of August, the last fruits are removed until the frost.
Store the collected fruits at a temperature of + 1-3aboutC and relative humidity 80-85%. Several times a month, watermelons laid in storage are examined, rotted and diseased are removed. For prevention purposes, the fruits are treated with milk of lime or chalk.
Fruits are placed on shelves with wide shelves. Shelves are covered with a layer of dry, soft litter 10-15 cm thick. For bedding straw, shavings, needles are suitable. Watermelons are laid in one layer, so that the fruits are not touching.

An example of proper storage of watermelons
The second option for storing watermelons is hanging in nets made of natural materials. This method avoids pressure sores and reduces the risk of developing fetal diseases.
Subject to storage conditions, the watermelon crop is stored for up to 3 months.
Since our weather conditions are not quite suitable for growing this berry, for the first couple of months our seeds sit under a spanbond. As soon as the third or fourth sheet is launched, we take it off. And water abundantly the first time. When the first flowers appeared, we water less intensely. Also, we simply tear off the extra flowers, then the fruits will grow more, verified. We have been planting this variety for several years now, it only makes us happy. True, it is not as sweet as is acceptable in Ukraine. I would be glad if my review is useful to someone.
astan kovihc, Belarus, Gomel
//otzovik.com/review_4552237.html
Since mid-August, I eat watermelon every day. So it's worth it. He regretted one hundred square meters of land, stocking up spanbond eventually increased a hundred pieces. Mostly small from one to two kilograms. Maximum four kg. But the taste is what you need. And most importantly, zero chemistry, which is typical. I advise everyone.
Sasha
//www.sb.by/articles/arbuzy-nam-po-plechu.html?commentId=204754#com204754
I hasten to share my impressions of the seeds of the "Crimson sweet" variety watermelon. My aunt brought these seeds to me this afternoon, she is planting the same ones for the third time in her garden. Watermelons grow medium size, the color of the pulp is not bright. But watermelons are really sweet. We were treated to aunt watermelons for two years, and now we will plant ours and we will wait for a good harvest. I put the five. I recommend to buy. Watermelons last summer at the aunt in the garden grew sweet even in the climate of the Republic of Belarus.
Tasha19, Belarus, Gomel
//otzovik.com/review_4820639.html
Growing watermelons in a Belarusian garden or plantation is not only interesting, but also useful. Cutting a watermelon grown by your own hands on your own personal plot, you can be sure that the crop grew without the use of chemistry dangerous to humans. Such a watermelon did not lie in the vegetable store, did not shake in the back of a truck on the gas-polluted freeways ... You can taste such a watermelon yourself and treat the children without fear of consequences. Therefore, environmentally friendly, farm products are appreciated. Today, to grow a varietal watermelon in a garden or in a greenhouse is a little more difficult than cucumbers or squash. The striped guest on the Belarusian beds confidently took his place, ceasing to be exotic.





















