Pruning grapes along with bait and watering affects the quality of fruiting and proper development of the vine. This event requires care and a reasonable approach. The process allows you to optimally determine the load on the plant, to form a bush depending on the varietal characteristics, the type of support and the geographical location of the garden plot. Properly pruned vine looks neat, decorative and has a high yield.
Do I need to prune the grapes
Cut old, sick lashes, growing incorrectly, to form young shoots, it is necessary in the same way as to feed and water the plant. The grape pruning procedure allows you to clearly adjust the load on the fruiting shoots (forming pruning), protect the plant from the adverse effects of pests and reduce the likelihood of infection of fruit crops (sanitary pruning). In practice, it is clear that the life expectancy, immunity and productivity of the plant also depends on this event. Pruning the vines will not bring trouble if you know the structure of the vine and the characteristics of the selected variety.
When to prune grapes
Sanitary pruning is carried out in the fall, in the spring a bush is formed taking into account the support and the load is regulated by clusters. In the fall, old, dried and damaged whips are necessarily cut, leaving a large number of eyes in stock (in case of damage to grapes by frost). According to the results of wintering in the spring, they are determined with the cutting length and the optimal crown shape is chosen.
Video: when to cut grapes
Autumn pruning of grapes
Autumn pruning is started 2-3 weeks after the end of the harvest. Pre-thin out the plant from dried leaves, old curves of perennial shoots, which will be removed without fail in the current season. And also remove excess, poorly matured and incorrectly growing lashes (in the middle of the bush and down). Only young shoots up to 7 mm thick with a maximum number of eyes (8-16 pieces) are left without damage. The final pruning in anticipation of wintering is organized after the first frost (the last decade of October - early November), at which time the vine on the cut becomes brownish and slightly crackles upon bending. The percentage of pruning is determined, focusing on the growth of shoots, in total, no more than 80% of shoots are cut. In accordance with the selected length, the required number of buds is left on the fruiting lashes of the next season. Preference is given to fruit shooters having a knot of substitution, and which can be easily and safely bent down and insulated for fruit eyes.

They try to remove the thickening shoots so that the remaining lashes can fully develop in the next season
In order not to weaken the plant in anticipation of frost, many gardeners carry out only sanitary autumn pruning. The formation of the fruit link begins only in the spring, when it is easy to distinguish between living and extinct buds.
In central Russia, autumn pruning is typical for table varieties that need to be covered for the winter, that is, to minimize the size of the bush. I cut off technical varieties (in my area - Isabella, Lydia, Raja) in spring, when there is a "cry" and immediately on the plant dry, brittle, non-overwintering (dead) shoots become noticeable.
Spring pruning
The purpose of spring pruning is to finally form the fruit link and give the plant a neat shape, directing it to a trellis or arbor. In the spring, the procedure is started before the buds open, but when the heat sets in - at a temperature not lower than + 10 ° C in the afternoon, when the threat of day and night frosts has passed (late March in southern Russia, early April - in the middle zone of the country). It is best to prune grape lashes in sunny, calm weather.
The vines that have proliferated last year are cut. Choose strong healthy shoots:
- 2-4 fruit shooters (3-7 mm thick) on table varieties;
- from 2 to 6 shoots (in diameter 4-8 mm) on technical grapes.
According to the biological characteristics of the variety, a long, medium or short pruning of the vine is carried out taking into account the load on the plant, form the fruit link.
Do grapes be cut in summer?
Vigorously growing crown of grapes requires close attention in the summer. In order for the necessary nutrients to be delivered to the fruiting shoots, and the clusters to be filled with sweet, juicy berries, summer pruning is required. It is necessary:
- regularly remove stepchildren (second-order shoots growing from sleeping buds);
- coinage - fatlique apical shoots are cut by 20-25 cm 2-3 times during the growing season;
- thin out leaves that thicken the bush too much and obscure the clusters (copious greens provoke the development of fungal diseases on the vine).

Stepchildren develop very quickly and take a small part of nutrients and moisture, so they are cut out during the summer every 3 weeks
How to prune grapes
Before starting the procedure, they prepare for trimming and stock up with the necessary tool. Before embarking on this crucial event, you should:
- specify the age of the plant;
- determine the support for fruit arrows;
- select the crown formation option.
During autumn and spring pruning, as a result, 50 to 80% of shoots of the grape bush are removed.
Video: how to prune grapes
Preparing the bush for pruning
Before pruning, the base of the stem is cleaned from old foliage and weeds, the surface dew roots are trimmed. After partial removal of the lashes that grow inside the bush, and thin unripe, as well as fattening shoots, the vines are removed from the support and carefully laid on the ground (in autumn). During spring pruning, the overwintered grapes are first fixed on a support, then the extra lashes are removed using a secateurs.
Basic Rules
In order for the fruit arrows to develop correctly, and the yield does not decrease, it is necessary to study some of the features of pruning the vine.
- Young shoots are selected on which the replacement knot is located on the outside. In case of its absence, shoots are formed on last year's developed lashes.
- Cut the fruit arrow along the internode 3 cm above the eye.
- The load on the shoot can be from 4 to 16 eyes, on the plant completely, from 25 to 30; on vigorous varieties - up to 45 ocelli.
- In autumn, the shoots are cut perpendicularly or at an angle, in the spring - always obliquely so that the apiary (sticky, viscous liquid secreted by plants when the shoot is damaged) does not flood the buds.
- Making a cut, the secateurs are placed with a sharp blade to the remaining part, a wide fixed knife (emphasis) is directed to the removed part.
- Pruning is always carried out from the outside of the bush so as not to disturb the natural sap flow.
- In order to avoid breaking off shortened shoots under warming (in winter) or under a load of bunches (in summer), they are bent at an angle to the hemp.

Neglecting the rules of pruning the vine is unlikely to destroy the plant, but you can easily lose the crop
How to form a fruit link
The main purpose of pruning is to correctly form the perennial skeletal part of the vine, on which the fruit link is located - last year's grape whip, consisting of:
- The knot of substitution is a short shoot, cut into 2-3 buds, from which the fruit link of the future vegetation period is formed.
- The eye is the buds from which the supporting shoots of this year's crop will grow.
- Fruit arrow - last year's shoot, cut according to varietal characteristics for a certain number of eyes. It is this shoot that bears the brunt of the harvest.

On the example of the formation of the fruit link on the bushes of four sleeves, it can be seen that each lash consists of a replacement knot and a fruit arrow
When trimming a knot of substitution, always make an oblique cut from the outside of the whip, while leaving 2-3 buds.
Video: pruning grapes to the fruit link
To form a fruit link, pruning of shoots of different lengths is carried out, taking into account the fruitfulness of the selected lashes: in the lower, middle or upper part of the vine.
- Short pruning - for 4-6 buds, choose for grapes with the most productive lower eyes. Often such pruning is used in greenhouse varieties and in vines with a high stem.
- Medium pruning - for 8-10 buds, it is suitable for medium-sized varieties, the main crop of which is in the central part of the shoot.
- Long pruning - 10-12 buds more often used for strong-growing powerful bushes of dessert grapes, as well as for pruning most technical varieties.
- Mixed pruning is carried out, for example, during the formation of a reinforced fruit link: the upper lash is cut longer (for example, by 10-16 kidneys) - it will bear an increased load of bunches, the lower one (we leave 4, 8 or 10 kidneys) - according to the biological characteristics of the variety , this shoot loads at the norm. Such pruning is suitable for grapes with well-developed bushes and painlessly tolerating the additional load of the crop.

In the figure, a variant of mixed pruning of grapes, in which short pruning is used for substitution knot (1) and medium (in the center of the bush), long (on the sides) for fruitful shoots (2)
Methods for the formation of grapes
Choosing the option of forming grapes, take into account the variety of vines. So, industrial grapes are often placed on an arch and a gazebo, and various types of cordon formations are suitable for the dining room. Be sure to take into account the age, frost resistance of the plant, the percentage of strain on the variety, how powerfully the stem and shoots develop (the distance between the plants in the row depends on this).
It is important not to forget about the technology of cultivation of grapes - vigorous bushes are often placed on strong trellises and high arbors and pergolas. But at the same time, it is taken into account that such a bush requires maximum attention - the area of nutrition and the volume of moisture grows several times, in contrast to medium-sized varieties, which grow well in standard and cordon form.
Powerful tall grapes give a lot of overgrowth, which is rather laborious to carefully clean on a gazebo or high arch, and without this the bush looks less neat, and yield decreases. If you want to decorate the site with a gazebo braided by vines strewn with bunches, this will require a lot of effort and financial investment. Regular top dressing and trimming with long garden shears, cleaning inside the gazebo, constant thinning of the bush (to exclude dampness and reproduction of any unpleasant insects) are provided. I was convinced from my own experience that such a formation requires much more attention than, for example, a standard or cordon. To have a decent "grape arbor", the best option is to plant one vigorous variety and give it maximum attention. If you plan to simply harvest, medium-sized varieties (2-3 varieties) formed on a horizontal or oblique cordon are suitable. They will take up no more space, labor and time than grapes on the gazebo.
The main methods of forming a grape bush:
- fan formation;
- standard and non-standard pruning;
- the formation of the vine on an arched vertical trellis and arbor;
- cordon pruning.
Photo gallery: grape bush formation options

- A full fan of grape bush is formed in 3-4 years.

- With a standard formation, the lower part of the vine bush takes up less space

- For the stemless formation of the vine, a reliable support is required for lashes loaded with bunches

- Arched grapes save space on site

- The grapes on the gazebo look very attractive, but require regular shaping pruning

- For table varieties with a large load of bunches, a cordon formation is often chosen
Fan formation of a grape bush
One of the easiest ways to trim and shape a grape bush is a fan. Suitable for young plants and oversized, for wine and dessert varieties. According to many winegrowers, fan shaping is simple and convenient. But also fan lashes are compact and decorative, it is easy to lay them in the fall for winter warming and in the spring to place them on a support of any height.
Fan formation is distinguished by the presence of several perennial fruit vines located at an angle to each other and cut to different lengths. Each lash has approximately 6 to 14 eyes depending on the variety. A knot of substitution may be absent, the crop of the next year in this case develops on one of the vines (the most powerful one located as close to the base of the bush as possible).
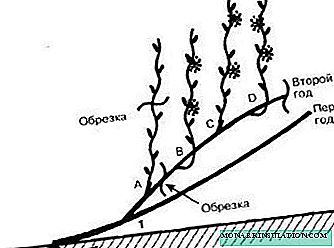
A two-arm fan is formed on the plants in the first year: the plant is cut into 3 buds and a knot of substitution is left on each branch. In the second year, you can leave two lashes or four (depending on the power of the bush). Starting from the third year, usually only four sleeves are formed, which can remain in the future, or, to increase the load on powerful grape varieties, whips can be added - up to 10 sleeves.
Fan shapes come with and without a stem. As a rule, a standard fan consists of fewer sleeves than a standardless fan.
Video: fan-shaped grape
Fanless formation of a grape bush
Grapes in a fanless fanless form are used in the cover viticulture zone. Such forms are easier to cover in the winter and rejuvenate after frost damage.
In the first year, the plant is pruned for reverse growth to reinforce and develop powerful lashes in the coming season. In the spring of the second year, a recess (10 cm) is made at the base of the stem, from which the trunk and tall shoots grow. And in the autumn of the same year, deepened shoots are sprinkled on for the winter, now the grape bush has two main growths in the form of lashes, tilted to the ground at an angle of 45 ° C - this is a two-arm fan.

Up to four shoots are left on the fan without a stem, on each of which two vines develop (one of them is the future replacement knot)
Fan forms are divided into a fan and a half-fan (one-sided fan formation). This allows you to leave up to four sleeves with a rejuvenating base on one side. There is a short-cut ground fan shape. It is used in the southern regions, where in the winter the stem is spud and cut.
L. SlepkoThe manual "School for beginner Siberian winegrower"
Grape Trimming
Hammer and combined pruning (shtamb + fan) gained popularity in the area with sharp temperature fluctuations, when frosts can come in a snowy winter, and sharp warming causes eyes to melt.
Vines are formed on a high perennial stub, which is insulated in winter (spud or wrap with non-woven insulation); shoots cut off as much as possible. Thus, such a formation is suitable in the zone of uncultivated viticulture.
In spring, shoots are subjected to short pruning (for 4-6 eyes). The lashes are hung down or tied to a support in parallel, to the ground or vertically - this depends on the load of bunches on the bush. In this case, the shtamb (70-150 cm high) serves as a support for productive shoots.
In the garden, grapes on the stem look decorative and compact.

Stacked grapes often look like a tree, regardless of the length of the stem
With a high load of the crop on the bush, the clusters are tied up and minted of young shoots and apical shoots of the stem.
Video: standard grape pruning
Formation of grapes on a two-plane trellis
The single-plane support is suitable for thin and medium-sized dessert varieties or for strong-growing in the first two years. In the third year, it is advisable to fasten the vigorous grapes to a more reliable support - on a two-plane trellis (vertical or inclined). A powerful growth and increased load, the one-sided support will withstand in any case, but the plant will be thickened and it is more difficult to care for such a powerful bush in one plane.
- The height of a two-plane trellis is traditionally 1.5-2 meters, the width between landings is at least 2.5 meters.
- Grapes having this kind of support are cut with a fan in compliance with the varietal load (more often medium-sized pruning is carried out).

Grapes on a two-plane trellis - this is the optimal load and minimizes the thickening of shoots
Grapes pruning
The formation of a bush of grapes on the gazebo encloses a vertical cordon and is suitable only for non-covering varieties. The plant is not only able to give an excellent crop, as with other forms of pruning, but also serves as a decoration for the building (pergolas, arbors, awnings) and the entire site. The "green cloak" of grapes shades well and protects against draft. The support for the shoots can be vertical welded metal rods or arcuate arches. An additional load is kept by wire fasteners when the maximum load is to be harvested (5-7 year old bush).

The main support for fruiting vines in the gazebo is the roof of the building
In order to rationally use the seat, while not changing the load on the bush, use a vertical cordon or four-arm fan. Most often, for arched and gazebo planting, technical or strong-growing frost-resistant varieties are used. Plants are planted around the perimeter of the walls of the support - in the center one plant (fan) or in the corners on each side (one-sided multi-tier cordon). Trimming is carried out according to the selected formation.
When pruning grapes for the gazebo, you can use any method of formation. The main thing is that grapes should not suffer from frosts, then a low standard and a cordon formation for any variety will do. Or a fan - for frost-resistant grapes. A stem up to 60-80 cm high and a multi-tiered formation with free-hanging shoots looks very beautiful and modern, even if the grapes grow only on one side of the gazebo.
Video: grape pruning on the gazebo and arch
Pruning grapes
Cutting the grapes for reverse growth, leave one or two buds for enhanced shoot growth in the upcoming season. The method is relevant for annual shoots: leave 5-7 cm of the stem and two shoots, when fan-shaped, pruning is carried out at a height of 8-10 cm from the ground. This pruning option allows you to increase the strength of the vine, the thickness of the shoots and reanimate a weak plant.
Video: grape pruning for reverse growth
Cutting grapes on the cordon
During cordon formation, grapes have a stem with a height of 80 to 150 cm and one or two sleeves located in the same direction or opposite to each other at an angle or parallel to the ground on a single-plane vertical trellis. On each lash, fruit shoots develop (1-8 pieces). The cordon can be multi-tiered or formed in one sleeve.
There are several types of cordon formation:
- Horizontal (surface) cordon. The stamp is of various heights, the lashes (2 or 4) are placed horizontally on different sides (double-sided) or in one direction (multi-tiered). Vigorous varieties are cut into 5-8 eyes, grapes of medium strength - 3-4 eyes. Each fruit arrow contains from 6 to 10 kidneys.

With a horizontal cordon, the height of the stem varies from 80 cm to 150 cm
- Vertical cordon: several tiers of two lashes are cut into 4-6 eyes and fixed horizontally; subsequently 2, 4 or 6 hanging shoots with clusters develop.
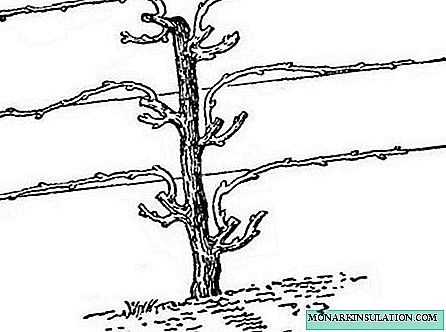
Vertical cordon is often used to form industrial grapes.
- With an oblique cordon, the lashes have an inclination at an angle of 45 °, trimming by 4-6 kidneys is preferable. With an oblique cordon, the tiered shoots are also not excluded.
An oblique cordon, if necessary, can be formed on one lash to save space
Video: grapes cut into a slanting cordon
One-sleeve method of forming grapes
When forming in one sleeve, an oblique or horizontal cordon is used. In the autumn of the first year, young lashes shorten a little, and in the spring in the second year they leave one shoot. Only the upper two buds are grown on it - a fruit shoot and a knot of substitution. The vine is tied up horizontally.
Single-sleeve grapes save space. The compact arrangement of the bush with one lash allows you to place several varieties of table grapes on a small garden plot in one trench.

The formation of the vine in one sleeve allows you to place the whips compactly
The formation of a long stem for grapes
Long-stem grapes are grown on a powerful single-row trellis (1.5 - 1.7 m) in a single stem with a height of 120-150 cm, while the optimal trunk width is at least 10 mm. With this formation, the shoulders in an amount of 2 to 6 are laid horizontally on the wire without a garter. 3-4 eyes are formed on the lashes, only 2 buds are left on the knots of substitution. Growth on shoots hangs freely.

Grapes on a long stem takes up little space and minimizes care
Grapes grow on a long stem more often in the zone of uncultivated viticulture and looks compact.
Video: the formation of a grape bush on a high stem
The formation of grapes around the world
Grape rows according to the rules of planting are sent to the east and southeast. The scourges are located from north to south. This direction is acceptable for cordon and fan formation. The grapes on the gazebo and arch and in the tall stem can have whips with the proposed direction, but for convenience, the vines are spread on all sides.
Grape Formation Four-Arm Fan
Seedlings trimmed in the first year for reverse growth, next year will give powerful shoots. They will become the basis of a two-sleeve fan in the second year. All subsequent years form a bush depending on the biological characteristics of the variety - from 4, 6 or 8 sleeves.
- In the autumn of the second year, 2 lashes in the center of the bush are cut to 30 cm (up to 4 eyes); at the edges leave long sleeves - 40-60 cm (6-8 eyes).
- The following spring, all but the upper two are blind. Of the remaining two ocelli, the upper one is the fruit shoot and the lower one is the knot of substitution.

Four-armed grapes in the first year of life
Each subsequent pruning is carried out similarly every year.

Grapes formed on four sleeves, 3 years after planting
If you do not leave a knot of substitution, 2 eyes should always always be on the shoots - the development of two fruit vines will not give an excessive load with such a formation.
Video: four-arm fan of the vine bush
How to rejuvenate old grapes
Perennial grapes often have unproductive thin shoots and can be very thickened. In order to rejuvenate the old grapes, the stem is cut at a height of 35-50 cm to reduce the load and future sleeves are formed from young shoots.
If it is possible to leave a shoot on which the fruit link will be formed - choose a whip no thicker than 7-9 mm, 3-4 buds and a knot of substitution are left on it. In the first year, the load on the old bush is reduced by 40-50%, in the next year it is brought up to 70%. Only in the third year a full bush is formed and the standard load for the variety is returned.
With complete rejuvenation - pruning to a black head - the skeleton of the bush is renewed due to sprout shoots in root vineyards or fattening ones on grafted ones. If a well-developed root system is present, this is carried out in 2-3 years, especially quickly when the bush is formed using stepsons.
K.V.Smirnov//www.nnre.ru/biohimija/vinogradarstvo_pod_red_k_v_smirnova/p7.php

Grape rejuvenation is the ruthless removal of 90% of the shoots
Grapes crying: what to do
Weeping vines - a natural physiological process of the vine bush, which does not require certain actions on the part of the vine grower. During this period, necessarily carry out the first water-charging irrigation in a moderate amount (15-20 liters per three or five-year bush).
The spring weeping of grapes marks a successful wintering of the vine. This process means that the plant has woken up and natural sap flow begins, soon the buds will burst and the first rudiments of leaflets and shoots will appear - everything will stop. "Crying" lasts from 30 to 50 days (sometimes until the appearance of 2-4 leaves). Abundant juice production occurs at the beginning of the growing process, when the ambient temperature rises to +7 +9 °C with enough moisture. Crying leads to a loss of nutrients and fluid (up to 15 liters), the plant during this period is weakened.

The abundant secretion of juice indicates the active life processes of the plant
The weeping process of the vine is harmless to the plant:
- If all pruning rules are followed (see above).
- To remove the lashes, a high-quality tool is selected.
- Crop timing respected.
- After trimming, there was no sharp drop in temperature.
If "crying" occurs for a long time on most vines, you must:
- treat the plant with fungicide;
- cover the slices with garden varnish;
- to constrict the whip with fishing line or wire.
When you can not cut grapes
The strength of growth and yield of grapes in the future depends on compliance with the timing of pruning. It is not recommended to cut shoots of any age:
- upon the occurrence of the first prolonged frost in the fall;
- with the beginning of active budding in the spring.

In order not to lose the grape bush, when pruning, you must follow the rules and not neglect the prohibitions
During autumn planting, young seedlings are not pruned (with the exception of the reverse growth). Lack of nutrients and moisture until the end of the growing season can cause the death of the plant.
Grape pruning in the regions
The climatic features and geography of the plant inevitably affects the timing of pruning and the formation of the bush.
Pruning grapes in Belarus
In late September or early October, the vineyard is undergoing sanitary pruning. Finally, Belarusian gardeners form a bush in mid-November, but always 10-15 days before the forecast frosts. In the early spring (in March), corrective pruning of the vine is carried out. Non-covering varieties are often cut only in the spring after the snow has fallen, but the buds are still sleeping.
In Belarus, the vine is formed on a stem and without, with a fan, and cut to a cordon. Winter hardy dining rooms and technical varieties on arches and gazebos winter well.
Grape pruning in Siberia
The northern climate with a short growing season forces the wine-growers to do heavy pruning, and only in the fall. Spring pruning is unacceptable, as the vine is opened gradually. In Siberia, unexpected frosts are likely until the end of spring, any grape variety will die under such drops. Therefore, the processes of vegetation and active growth begin on grape lashes before they are completely freed from insulation and fixed on a support. At this point, the grape bush should be finally formed.
Here, a fan formation on two sleeves (they are easy to cover for the winter) or on four lashes and a cordon (oblique and horizontal) is preferable.

Fan-shaped formation simplifies the preparation of the bush for winter and its warming
Pruning grapes in the Kuban
On the territory of the Krasnodar Territory, all types of trimming and shaping listed above are acceptable. The vine bears fruit well and tolerates wintering on the arch and gazebo, cordon and fan formation shows an excellent result in the yield of shoots.
The southern climate calls not to rush with pruning in the fall, and hurry to form bushes in the spring before the sap flow begins. In the zone of uncultivated viticulture, bushes at any time from the onset of leaf fall to severe frosts - from the first decade of November to mid-December.

If the weather doesn’t fail in the south of Russia, the grapes are cut before the end of December
Sometimes in autumn only sanitary pruning is carried out, the bush is finally formed in March, but before the onset of active sap flow (before the "crying" of the vine). Technical and early ripe table varieties, in which the growing season begins early (with the first warming), are cut only in the fall, while immediately forming lashes on the fruit link.
Reviews
The formation for the gazebo is very similar to a horizontal cordon. The difference in height of the stem. The shoulder is formed at your discretion. It is necessary that the greenery is located higher - let the first wire from the ground 1-1.5 meters. If necessary, place it at a distance of 40 cm. Next, the sleeves are formed by each upper kidney. That is, 1,3,5,7,9 ... then everything too. Here are just cropping no more than 3 kidneys. And the arrows do not pinch if you need a canopy.
Belikova Galina//www.vinograd7.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=32&sid=0bf96864ad40f05cfecd14b05aa76d8b
As we know, there are more than 20 formations. In my opinion, the horizontal cordon is one of the most successful today. Firstly, it is convenient to shelter bushes for the winter. Secondly, it is convenient to carry out processing, an ideal approach to the bushes. Thirdly, the prospect of growing a huge (not afraid of the word) crop. I will help to understand this formation. To do this, plant a bush and build a single-plane trellis (for a start, consider this option). For some winegrowers, it is more convenient to grow a bush without a trench by planting a bush on the surface of the earth and making a near-trunk circle. For this situation, the first wire on the trellis extends about 40 centimeters above the ground, the second also about 40 cm from the first wire, the third about the same. The latter should correspond to your capabilities, in other words, it should be positioned in such a way that you can attach the shoot to it with outstretched arms. Under ideal conditions, we should have 2 shoulders and 5 sleeves on each shoulder for the season.
Svetlana//www.vinograd7.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=16011&sid=0bf96864ad40f05cfecd14b05aa76d8b
In our northern latitudes, you don’t have to choose - most varieties grow along the walls, and you can only cover the fan in winter. The wall is from west to east, the vine is 2-3 meters, I cut it for 8-10 buds, the fan grows normally, and in the open place only sleeping buds wake up and then barely, although the vine ripened 2 meters that year. Therefore, building a fence with a canopy, grapes from the north wind will be closed to them, I hope this helps.
Vladimir 2//www.vinograd7.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=747&start=10
It is necessary to cover the cuts when cutting when they dry out, and it is better to runnet - moisture does not linger under it. If you smear with var, then it is only melted, as if impregnating the cut wood, and this must be repeated, as the cut will crack. Cold var lap is a source of dying of bark and fungal infections. The main thing is to make sure that the grape juice does not get on the kidneys. There is a lot of sugar in it, and after such "processing" the kidney may not open. Sections are directed so that it flows past or immediately into the soil.
Tatyana//forum.vinograd.info/archive/index.php?t-93.html
The young are shortened and old, dry lashes of grapes are cut every autumn and spring. How best to do this, each gardener decides for himself, taking into account the characteristics of the variety, the growth power of the plant and climatic features. If grapes grow on your garden plot, it means that over time you will definitely have to master the subtleties of pruning this plant. This will help to affect the yield and taste of berries of both technical and dessert grapes of any age. The process of pruning grapes will not be difficult, on the contrary, it will become a fascinating process, an occasion for experiments with bush forms and types of trellis.




















