Onion-batun is a perennial vegetable that continuously supplies vitamin greens to our table. It is so easy to grow that once you have settled a batun in the garden, you can only occasionally update the plantings, and you only have to worry about their safety except in the conditions of the Far North. Batun is used in all dishes, but the main thing is the early greens, which appears one of the first.
Plant description
Onion-batun is a herbaceous plant that can grow in one place for many years. Outwardly, in the garden, it looks the same as most onion plants: the same fancy leaves are green in color, often even called cricket onions. Chinese is also its name, because in China and Japan, as well as in some places in Siberia, it grows in the wild.
However, unlike the well-known onions, there is nothing to take for food under the batun: the onion is very small, and even, rather, not a bulb, but only a small thickening. In principle, it is edible, but only leaves are used for food. They contain many useful substances for the human body: sugars, essential oils, vitamins, trace elements.
The content of ascorbic acid in the leaves of onion-batun is twice as high as in the leaves of ordinary onions.
Onion-batun without problems grows without transplanting for several years, and with proper care 5-6 years for him is "not a deadline." However, then it becomes more difficult to take care of the thickets, and planting is rejuvenated. In harsh climatic regions, it is sometimes planted in greenhouses, but the main place of residence is open ground, where it feels great in any locality.
Several subspecies of a batun are known (Russian winter, Japanese, etc.), and Russian is considered the most frost-resistant: it can withstand temperatures up to -30 without shelter aboutC, and leaves during the growing season - up to -8 aboutFROM. This perennial plant begins to grow its leaves as soon as spring temperatures take positive values, that is, in fact, soon after the snow melts.
Neither increased humidity nor the proximity of groundwater are terrible for a batun, it feels uncomfortable only during a prolonged drought. Despite the long-term nature, sometimes it is grown in an annual culture. Already in the first year it gives a good harvest of succulent green leaves, which are slightly larger in size than the leaves of onions: their height is up to 40 cm with a diameter of 2-3 cm. It is also famous for its developed roots that can spread in and out up to 40 cm.

Onion plants look powerful: it has large leaves and long roots
The complex chemical composition of the rod gives it a certain burning taste. Compared, for example, with chives, the batun is less sweet, although it is also quite tender and no less useful. An extract from the juice of this onion is even used in pharmaceuticals, since it helps to lower blood pressure. In Chinese medicine, the batun is considered a cure for a variety of diseases, it has an effective disinfecting effect.
At the same time, as with other green vegetables, the calorie content of this onion is low. Its nutritional value consists, first of all, in medicinal properties. Batun is useful for people with impaired functioning of many internal organs: kidneys, liver, heart. It is used for gout, hypertension, dysentery, etc., it is a good diuretic. Not recommended batun, as well as other types of green onions, for people with diseases of the stomach, pancreatitis, gastritis.
Varieties of onion
There are several dozen varieties of onion, but the differences in consumer properties are small. Almost all varieties give greens of the same chemical composition, in general, their application is the same. The differences are mainly in yield, harvest dates and relative severity of taste. Some varieties are more, others less resistant to disease. All varieties are recommended for all climatic regions.
The first records in the State Register of the Russian Federation on varieties of this culture appeared in 1981, the last are dated the current year 2018. So, varieties with the speaking names April and May were among the first to be registered.
- April is an early ripe salad variety. Leaves remain soft and juicy for a long time, with a semi-sharp taste. The yield is good: the mass of the plant can reach 300 g. The disease resistance is very high.

April - one of the most famous varieties of batun
- Maisky - the variety is ready for use much later than April. This variety is also not affected by disease, it also gives high yields of greenery, but the feathers are thinner and taste sharp. From the beginning of seedlings to the death of feathers takes about 5 months.

Maisky is a late variety of batun, it belongs to the acute variety
- Long Tokyo is a relatively new mid-season variety, grows to a height of 60 cm, gives dark green leaves with a slight waxy coating. Leaves of acute taste, productivity is relatively low. It has increased winter hardiness.

Long Tokyo - a tall variety
- Tenderness - a salad grade of medium ripening: leaves are ready for cutting one month after the start of regrowth. The leaves are relatively small: up to 35 cm long and not more than 13 mm wide; wax coating is weakly expressed. The mass of the plant is only about 50 g, but the total yield per square meter is not bad. The taste is slightly sharp.

The tenderness differs, according to the name, with a rather mild taste.
- Russian winter - mid-season salad variety. The leaves are rather thin, not thicker than 1 cm, about 33 cm long, with a slightly sharp taste. Their color is lighter than most other varieties, the wax coating is medium, the taste is excellent. Average productivity: for the whole season about 3.6 kg / m2since it allows no more than 2-3 cuts per summer. Winter-hardy.

The variety Russian winter leaves are slightly lighter than other varieties
- Seryozha is an early ripe variety, leaves are tall (more than 50 cm), about 15 mm in diameter, bluish-green in color, wax coating is strongly expressed. The taste is semi-sharp, delicate. Winter hardiness is high, productivity in one cut is up to 2.8 kg / m2.

Variety Serezha leaves with a slight blue tint
- Fat-leaved - a variety included in the State Register of the Russian Federation in 2018, with an average ripening period. The leaves are dark green, wide, more than 40 cm long, about 2 cm in diameter. The wax coating is strong, the taste is semi-sharp. Productivity is above average, winter hardiness is good.

Fat-leaved is a fairly new variety of batun; information on early maturity of seed producers differs from the data of the State Register
How to grow onion
This onion propagates both by seeds and vegetatively, moreover, both methods are simple and are equally used in gardening.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
If the garden already has a onion-batun, it makes little sense to re-sow it with seeds, because for propagation it is much easier to dig a bush, divide it into smaller parts and plant it. At the same time, rhizomes of weeds can easily be pulled out of it, which eventually grow in the middle of the bush and inhibit it.

You can divide the bush of onion-bat into any number of parts, it is very simple to do
The division of the bush is possible almost at any time, but it is much safer and more reliable to do this in August. The bush is carefully watered and with the help of a shovel or garden pitchfork removed from the ground. Hands or using a conventional knife, divide it into small parts; in principle, it is possible to separate bulbs, but fragments including up to a dozen of them can also be planted. Bulbs are planted in rows according to the scheme of 8 x 25 cm, to a depth of about 3 cm.
Seed propagation
Seed propagation is a method that does not differ at all from that in the case of other types of onions. You can call it the main one, especially for those gardeners who plant a butt for the first time. Seeds can be bought in a specialty store or asked for at the neighbor's house, and they can be sown both in spring and summer.
Video: on the propagation of onion-batun
Growing onions from seeds
Onion-batun most often sown directly in the garden. Sometimes in spring, seedlings are also grown to quickly collect the first crop. Despite the fact that the batun is a perennial plant, some gardeners prefer to grow it as an annual. In this case, a normal crop can be obtained only through seedlings: after all, in a multi-year variant, maximum productivity is achieved only after 2-3 years.
How to Collect Onion Seeds
Collecting onion seeds is easy. From the second year of his life, he gives numerous arrows with peduncles, which, so as not to decrease the yield, are constantly broken out. These arrows on several bushes should be left. In the middle of summer, they will bloom, then seeds will appear in them. When they are almost mature, that is, they will turn black in color, but still hold on firmly in inflorescences, the plants are pulled out and suspended in bundles "upside down" in a dry room, substituting any dish under them or simply laying out a sheet of paper.
When the seeds dry, they themselves will begin to spill out. At this time, they are very easy to extract. Seeds are dried for several more days, spread out in a thin layer, and then poured into small paper bags for storage. The germination rate of onion seeds is small: with proper storage (in a dry, dark place) a maximum of two years.
Growing Onion Seedlings
Seedling cultivation of onion-batun is used in the case when the entire cycle from seeds to complete harvesting with pulling out plants is carried out in one season. In the perennial version, seedlings are not grown. Seeds are sown in April, grown seedlings are planted in the garden in early summer, and in September they completely dig out the plants and use them for food.
Sowing seeds for seedlings
To accelerate the germination of seeds, they are soaked in water for a day. Sometimes they are first etched for 20-25 minutes in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. During the day, water is changed several times, after which the seeds are slightly dried and sown in seedling boxes.

Batun seeds look just like any other onion seeds
The soil is a mixture of turf land with humus (1: 1) with the addition of two glasses of ash in a bucket of the mixture. Seeds are sown to a depth of 1 cm in moist grooves, but after falling asleep with earth, a two-centimeter layer of clean sand is also poured on top. In glass-covered boxes at room temperature, prepared seeds germinate after 2 weeks or a little later.
Seedling Care
Caring for seedlings of onion-brass reminds this activity in the case of most vegetable plants. So, immediately after the emergence of shoots, a sharp decrease in temperature is necessary: its week is kept at 10-12 aboutC, after which they raise it a little. However, the temperature is above 15 aboutC for onion seedlings is fatal, so growing it in a city apartment is very problematic. It is necessary to equip the backlight: the batun is a plant of long daylight hours.
Irrigation is needed rare and moderate: it is impossible to fill with water before swamping. During the cultivation of seedlings, it is fed twice. The composition of the solution for top dressing is 2 g of superphosphate and any potassium salt per 1 liter of water, the time of top dressing is 7-10 days after emergence, and then another two weeks later.
If the seedlings are thick, they must be thinned out. They do this in the phase of the first real leaflet, at this moment they leave a distance of about 3 cm between the plants. Before planting in the garden, a week before, the seedlings are hardened. It is planted in a bed at the beginning of summer, preparing holes at distances of about 12 cm from each other.

Seedlings of onion-batun are very tender, it is not too easy to grow it, so they do it relatively infrequently
Since the seedlings of the batun need coolness, it is possible to recommend such a method of growing only in the presence of an unheated greenhouse or hotbed, where you can maintain a temperature of 10-15 in April-May aboutC: at home, the labor expended is too large. Therefore, even for annual cultivation, it is worthwhile to prepare seedlings in a separate bed, having previously covered it for heating the earth with a film. Most varieties of onions and in such a situation will have time to give a good harvest of feathers.
Sowing seeds in the ground
Sowing seeds directly into the soil is the main method of seed propagation of a rod. If you sow them under the film in early spring, a normal crop can be harvested in August. Another option is sowing in June-July (for the middle lane). In this case, the plants will have time to become stronger in the year of sowing, and leaf cutting will be possible only next year. Winter sowing is also used, but it should be more dense, since many seeds will disappear during the winter.
It should be noted that the onion-batun does not like acidic soils and peat bogs. Sandy loam and loam are best suited for it, but it is important that the site is well lit. Preparation of the garden - as for most vegetables: preliminary digging with the introduction of conventional doses of organic and mineral fertilizers. Per 1 m2 this is a bucket of humus, a glass of ash and 10-15 g of superphosphate, potassium chloride and any nitrate.
Seeds are prepared, as well as for growing seedlings. They are sown in grooves shed with water to a depth of about 2.5 cm, the distance between the rows is about 30 cm. If the soil has already warmed up to at least 5 aboutC, the seeds will certainly germinate, but it can be stretched in time: from 8 to 20 days. It is advisable to mulch the bed immediately after sowing with a thin layer of humus. When it will be clear how many seeds have sprouted, the seedlings are thinned out, leaving about 10 cm between the plants.
Video: spring sowing of spring onion
Care for the Onion
Caring for this onion is simple: you need to try only at first. Crops are thinned out depending on how many years the bed is planted. For annual crops, thinning is required to a minimum extent; for multi-year thinning is carried out 2-3 times. Systematically, during the first year of life of the onion-batun, the bed is weeded and loosened. The rest of the care consists of watering, fertilizing and timely cutting of the pen.
Watering
The soil should be kept moist but not marshy. Short-term drying is not fatal, but in the case of prolonged drought, the leaves coarsen and become tasteless. Batun is watered 1-2 times a week, depending on weather conditions. Water consumption - about 1 m bucket2, temperature does not matter. Abundant watering of onions is required 2-3 days before harvesting.
The onion also tolerates sprinkling, especially in the adult state, but it is better to water it superficially, not feathering too much, since many of them can break when sprinkling. While the plants are not overgrown, after irrigation or rain the soil is loosened. When the bushes almost close, loosening becomes impossible, it is replaced by mulching the soil with humus.

You can water onions from a watering can, but you should not use a hose with a strong pressure
Top dressing
Topping onion-batun is carried out infrequently, but after mass cutting of leaves they are required. The best recipe in the first year is mullein infusion (1:10), and after it is absorbed, a glass of wood ash per 1 m is also added2 beds, closing it up with a shallow hoe. After any top dressing (and in front of it, too), the bed is abundantly watered with water.
In the second year, the mullein infusion is used already more diluted (1:15), but the ash is not limited in ash. If the soil is fertile, it grows well for several years without fertilizing. Actually, the onion itself signals a lack of nutrients by a slowdown in growth and yellowing of the leaves. As an ambulance, a weak solution of urea (a tablespoon in a bucket of water) can be used.
Pruning
You should not be afraid to cut off the leaves of the batun at any age, but the mass cut is done when the feathers reach a length of at least 20-30 cm. - up to five. For most varieties, the maximum yield is observed at 3-5 years of age.
Is it possible to trim the onion so that nothing is left on the plant? It is possible, but not worth it. A small number of young feathers are best left in place. So the plant will quickly recover its strength. Some gardeners cut leaves down to the very frosts. This is also a very bad option: in winter, the plant must be left with leaves. It is clear that in the winter they will die, and in the spring they will need to be removed from the garden. But they will support the strength of the onion in the late fall.
Growing onion-batun at room conditions
This plant practically does not know the rest period, which allows its year-round cultivation to be applied. It is possible in greenhouses, and, if necessary, at home. Although, of course, temperature limitations make this option not very simple. On the balcony you can get a harvest of greenery from April to October. But the windowsill should be cool, and then 1-2 years the onions will yield a crop year-round.
When warm, the plant will be pampered, and the crop will be sparse and less juicy.
Seed preparation is carried out in the same way as for the garden. Fertile loose soil is poured into any deep boxes or pots and the seeds are sown to a depth of about 1.5 cm. Water well and cover the crops with glass. After emergence, the main thing is light and coolness. Ideal after a week of cold (10-12 aboutC) - daytime temperature in the range of 18-20 ° C, nighttime - a few degrees lower. To the sunlight in the autumn-spring period, illumination with phytolamps is sure to be added.
At home, it is easy to monitor the soil moisture, so it is never overdried. For irrigation use settled water at room temperature. To avoid accidentally overmoistening, a drainage layer (small pebbles, sand) must be placed in the box or simply made holes in the bottom. Air humidity is also important: the optimum value is about 75%.

Any convenient container can fit at home for growing a rod.
Every two weeks, the batun is fed with weak solutions of complete mineral fertilizers (according to the instructions, but better less than more). From time to time it is useful for this purpose to use and infusions of any herbs. When grown at home, the leaves of a batun are cut, as a rule, not all at once, but selectively, as necessary.
How to use onion as a fertilizer
There are plants, both garden and wild, that perfectly fulfill the function of fertilizers: these are many legumes, oats, vetch, etc. They are called siderats: without bringing the matter to bloom, the crops of these crops are cut and plowed into the ground, significantly increasing its fertility.
Onion plants are not included in the number of siderates, but after the batun has served its term, many gardeners do not pull out the plants, but dig up the bed with them. Those nutrients that the onion has accumulated during its growth remain in the soil. Moreover, this technique also heals the soil, since any onion plants secrete a huge amount of volatile, killing pathogenic microbes around them.
Diseases and Pests
Most varieties of onion are very resistant to disease, but often suffer from some pests. Among the diseases encountered, the following can be noted.
- Viral mosaic is a dangerous, incurable disease. Carried by aphids. Ill plants have to be destroyed. The virus appears as yellow spots of various shapes, scattered across the leaves. Onions very quickly stop growing and then die.

Mosaic, like most viral diseases of plants, is practically untreated
- Leaf rust is a fungal disease: yellow-orange spots appear on the leaves. These are colonies of fungal spores that mature soon, causing the leaves to dry quickly. Damaged plants are removed, and unharmed sprayed with Fitosporin solution or Bordeaux fluid.

From rust you can save plants that have not yet had time to get sick
- Powdery mildew is a non-fatal but unpleasant fungal disease, manifested in the form of rapidly growing white spots. The diseased plants are destroyed, and healthy ones, as in a rust disease, are sprayed with solutions of copper or Fitosporin preparations.

Powdery mildew of onions, like most fungal diseases, is treatable, but it’s better not to bring it
Pests can completely destroy onion plants, so you need to deal with them on time.
- The onion weevil (crypto-scavenger) is a small dark beetle less than 1 cm in size. Its larva is a dirty yellow caterpillar. Both the beetle and the larva gnaw leaves, which eventually dry out.

Onion weevil is similar to any other weevil in the presence of a proboscis
- An onion fly lays eggs on the plant, from which larvae appear in early summer. They devour the bulbs from the inside, causing the batun to die. Since the onion fly does not tolerate the carrot smell, carrots planted on an adjacent bed reliably repel it.
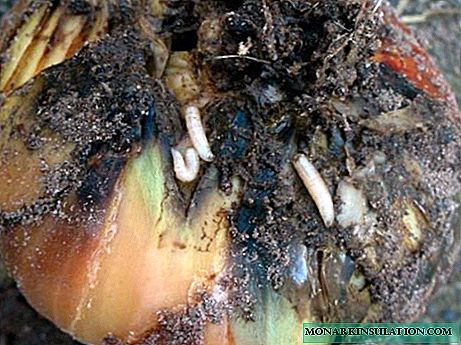
Onion fly larvae destroy mainly bulbs
- Thrips are very small light insects (up to 1 mm in size). Thripses harm not only onion plants, these creatures in one way or another annoy almost all vegetables. Larvae feed onion juice, as a result of which plants can die.

Thrips - small sucking insects that harm a variety of plants
Treatment and Prevention
Unfortunately, combating diseases and pests on perennial bows is more difficult than onion. After all, leaves are constantly used for food, which means that chemical control agents are not applicable here. Fortunately, the diseases of the batun are very rare and are treated mainly by relatively harmless means.
Folk remedies are often sufficient to protect against pests. For example, not bad, although not very effective, mustard powder repels many pests, which are sprinkled with a bed between the rows of a rod. Well repels pests decoction of tobacco. Having added laundry soap to it, periodically sprayed with this solution of the plant.
The most reliable prevention is strict adherence to agricultural technology: crop rotation, timely watering and loosening of beds, weed control, because many pests first settle on weeds, and only then get onions.
Possible growing problems
Onion-batun is very easy to grow, but sometimes gives the owner some inconvenience. It cannot be said that it is difficult to solve them: sometimes you don’t even have to do anything, but you just have to put up with the fact that the observed phenomenon is completely natural for this bow.
Onion turns yellow
Immediately after winter, the batun grows with bright green juicy leaves. But toward mid-summer, they may begin to turn yellow; usually the process starts at the very tips. Most often it turns out that nothing terrible happened, just the gardener began to forget about this plant and did not water it on time. Lack of moisture is the main reason for yellowing of the onion. Fortunately, the process is reversible, and if you pay attention to the garden again, yellowing will pass over time.

The yellowing of the tips of the onion feathers, as a rule, is not a disease and is easily eliminated by proper agricultural technology
The second commonplace reason is that onions spent all their nutrient reserves, it’s just time to feed them. The easiest and quickest way is urea, but better with complex fertilizer. Do not want to pour "powders"? We'll have to cook herbal infusion, better from nettle, but it takes time ...
Generally speaking, the defeat of the onion fly often begins with yellowing of the tips, and the mosaic manifests itself as yellow spots. Therefore, it is worth taking a closer look: is it a pest, is it a disease? If so, it is more likely to take action.
The bow goes into the arrow
The fact that a long-term batun forms an arrow for the second year and beyond is completely normal, only the first year of its cultivation can do without shooting. You can constantly break off these arrows, slowing down the aging of the onion, but it is impossible to completely deprive him of the process that is supposed to be in the life cycle. Shooting almost does not worsen the taste of young leaves that grow constantly, but nevertheless it should be recognized that the most delicious greens are in the spring and early summer. Or maybe it just seems, because at this time the body especially needs vitamins?
Harvesting and storage
The frequency of harvesting the onion-batun slightly depends on the variety, but in general it can be said that in most cases a complete cut of the leaves is possible every 3-4 weeks. A few feathers in a salad, of course, can be cut off at least every day. It is economically feasible to cut off almost the entire foliage when it reaches a height of at least 25-30 cm, and flower arrows, if they are not needed, almost completely break out immediately when they appear.
You can cut the leaves with a sharp knife or scissors, almost near the ground. The last time they can be completely cut off a month before the onset of frost. The green leaves of the rod are stored in the refrigerator, bundled or simply placed in a plastic bag, closing it loosely. Shelf life of fresh foliage is short, about a week, but it can be cut and frozen. In winter, thawed batun can be added to the first or second courses, it goes perfectly to the filling for homemade pies.
Onion-batun - a representative of perennial bows - is very convenient for planting in personal gardens. With almost no care, he delivers early vitamin greens to the table, and with elementary care, its yield is significant. The usefulness of the leaves of the batun for the body and the simplicity of cultivation allowed the culture to deservedly take a strong place among traditional garden crops.
























